All uploaded files are strictly confidential.
All uploaded files are strictly confidential.
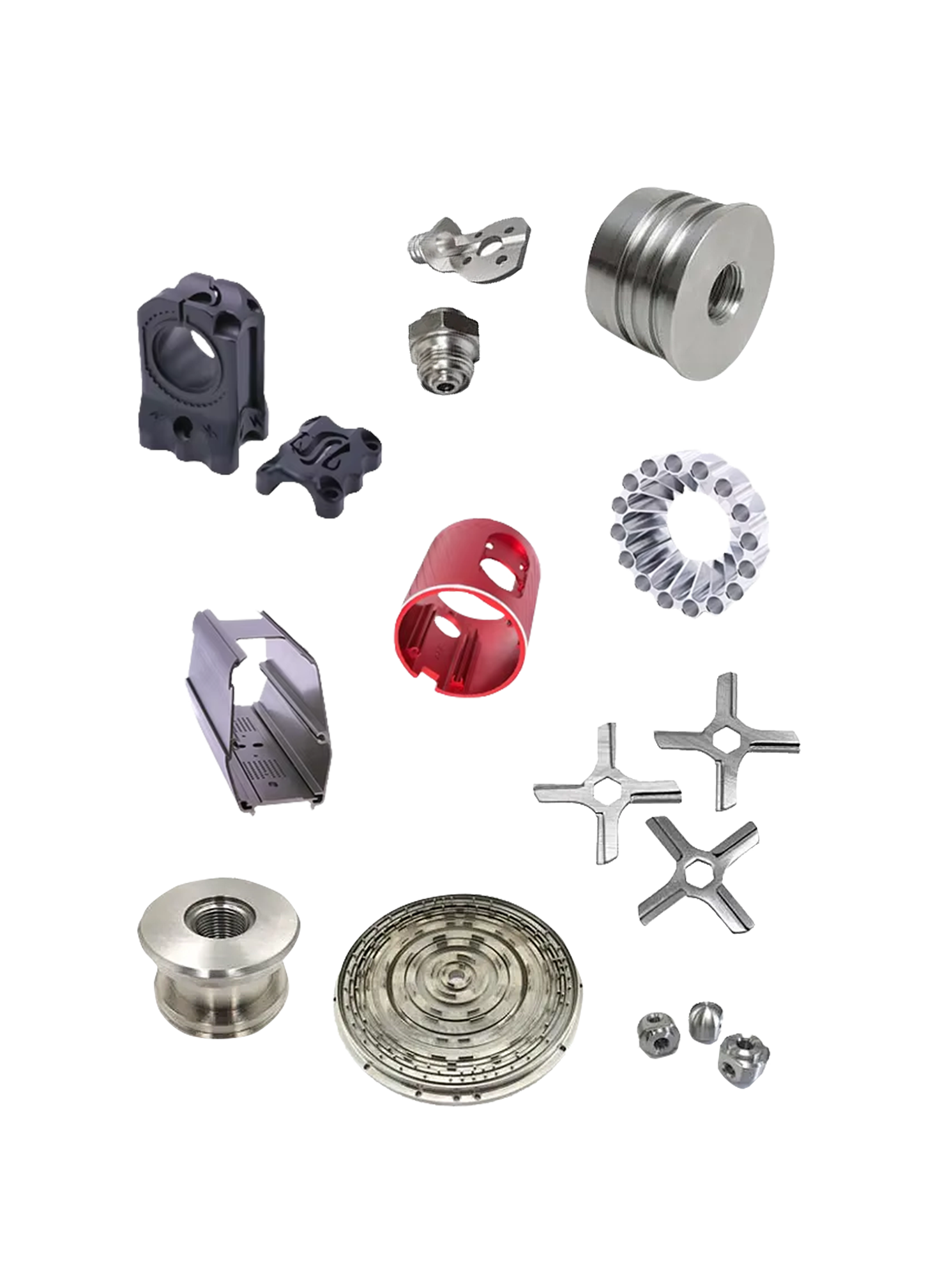
AI-Powered Flexible Manufacturing
Get Instant, Accurate Quotes
3D printing & CNC machining for rapid prototyping and small-batch production.
AI-powered instant quotes, online ordering, and secure workflows to cut costs and boost efficiency.

 中文(中国)
中文(中国)